Data Science
Thanks to Data Science you can extract information from all data coming from business management software such as ERP ( enterprise resource planning ), CRM ( customer relationship management ) or SCM (supply chain management ) and the recent entry of industry 4.0, both small and large companies generate a huge amount of data that, once analyzed, can provide great value. The competitive advantage it confers is of such magnitude, that those companies that do not adapt to the digital transformation will find very difficult to survive.
Nowadays only the 0,5% of all data generated by companies is analyzed according to a MIT survey.
Thus, through a Data Science project, a company can increase its revenues thanks to product recommendations and customization of the purchase process with customer segmentation or reduce your costs through more efficient purchasing planning thanks to demand prediction, optimized routes, personnel management or predictive maintenance.
In our Study Cases you have some real cases that we have done with innovative companies.
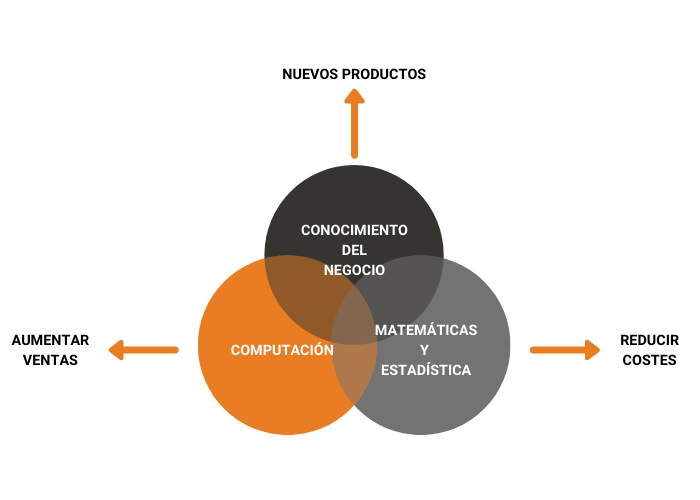
What is Data Science?
More detailed, Data Science combines computational, mathematical and statistical methods with the knowledge of a sector or industry, to extract from the standard data that will allow to predict or automate processes. This enables companies to reduce costs, increase sales and, in certain cases, create new products.
Data Science makes intensive use of Artificial Intelligence to provide solutions to problems of various kinds. For example, it is possible to use classic Machine Learning algorithms to predict the demand for a specific product, or in more recent Deep Learning techniques to automate complex cognitive tasks such as image classification or autonomous vehicle driving.
Data Science Applications
Data Science is a cross solution suitable to any type of business with multiple departments.
Demand forecasting
Recommendation system
Predictive and prospective maintenance
Customer clustering
Shrinkage Reduction
Prediction of product delivery delays
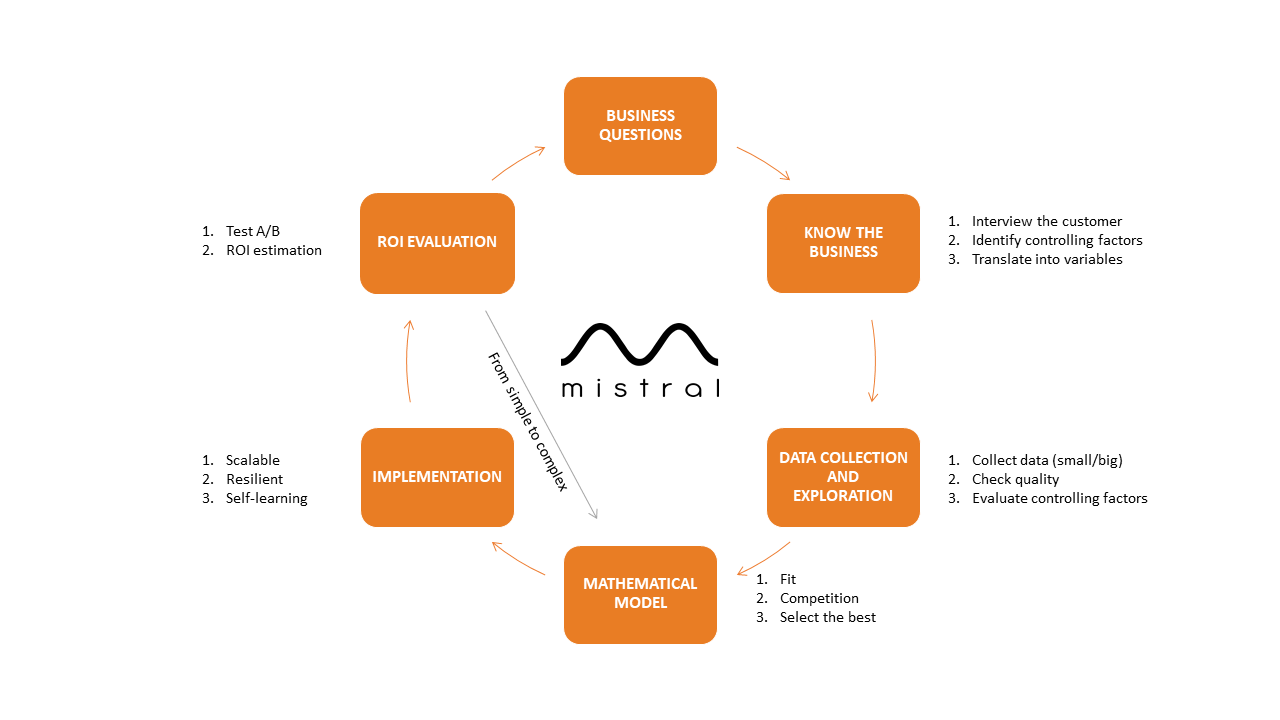
Business Questions
Our customer may manifest a need, whether a specific one to their own company or a more general one common to a sector, usually with its goal in reducing costs, increasing revenues or creating new products.
Know the Business
Mistral collects as much information as possible to answer these Business Questions and identify controlling factors and bottlenecks.
Data Collection and Exploration
Once the business processes are known and the control factors are identified, we translate this information into variables and data. Then an exploratory analysis is done to value its quality.
Mathematical Model
We apply Machine Learning methodologies to develop models that compete to see which one is the best. We start with simpler models so we can offer a faster response to customer needs and he/she can identify benefits as soon as possible.
Implementation
When we have a minimum viable model, it is introduced into the company's control system to learn continuously, with a scalable implementation and capable of training itself as it has more data.
ROI Evaluation
In the last phase, the revenue on investment (ROI) is evaluated, since the best mathematical model does not have to be the one with the greatest benefits. If ROI is lower than 0 we would return to the mathematical model phase to improve it.
Once the minimum viable model is implemented, the cycle continues with the development of more complex mathematical models that will replace the one previously installed if it is considered that it can reduce costs or increase profits. In addition, as more data or new variables are obtained, the goodness of fit index and ROI will be reevaluated each time.
In this phase Mistral monitors the real effectiveness of the algorithms developed by implementing dashboards (integrated or not in the control system), visualizing interactive and real-time evolution of the most significant parameters. In the following link you have more information about the Life cycle of a Data Science Project (Spanish).